Understanding Human Perception of Robot Appearance
Human perception of robot appearance plays a significant role in how we interact with these machines. The way a robot looks can influence our comfort levels and our willingness to engage. Anthropomorphism is crucial here; we tend to assign human-like characteristics to robots, which can affect our perception of them. An endearing appearance might elicit warmth, while a more mechanical form might lead to discomfort or wariness. Our brains are wired to react differently depending on what we see, leading to varied interactions based on the robot's design. The rise of Human Like Robots has further prompted discussions around their design and acceptance in society.
Cultural influences also shape our preferences regarding robot appearances. In some cultures, robots that resemble humans may be more accepted, while in others, a more functional design is preferred. Moreover, factors such as historical experiences with technology and media representations can affect perception. Age and gender further complicate this landscape. For instance, younger individuals might embrace humanoid robots more readily than older generations, who might view them with suspicion or skepticism. Similarly, gender can influence preferences; studies show women may prefer robots that display more nurturing characteristics, while men may lean towards more robust designs.
Elements of Robot Appearance Affecting Human Interaction
The physical form and size of a robot are critical in shaping our interaction with them. A robot's stature can either intimidate or comfort users. Generally, smaller robots tend to be perceived as less threatening, allowing for more positive engagement. On the other hand, larger robots may evoke feelings of awe or fear, depending on the context. Design elements like the outline and proportions contribute greatly to these perceptions, simply by aligning with our expectations of safety and approachability.
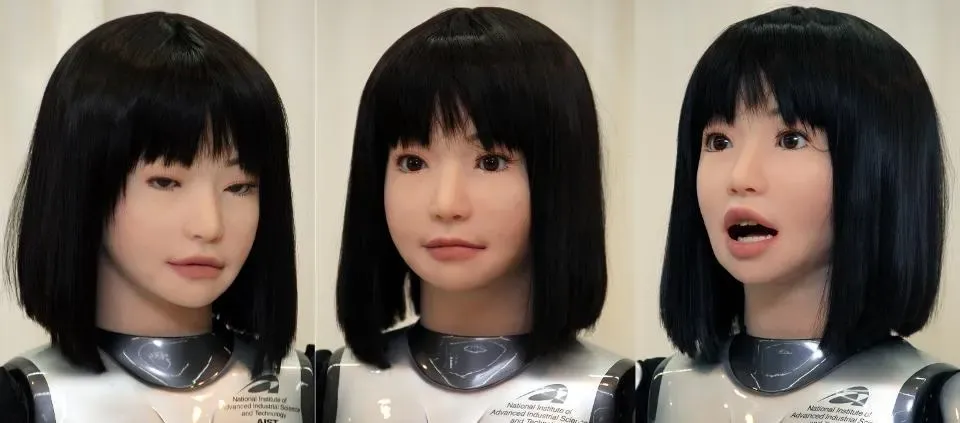
Another element that affects interaction is the robot's facial features and expressions. Our affinity for emotional cues drives this aspect of design. Robots with expressive faces can convey emotions and intentions, facilitating better communication. For example, smiling robots can create a welcoming environment, encouraging users to interact. Conversely, a robot with a blank face may not inspire the same level of trust or engagement. The subtleties in color and material choices also play a role. Bright colors may evoke a playful vibe, while metallic or darker patterns can appear more serious or even hazardous. These design decisions can directly sway a user’s emotional response and willingness to interact.
Mobility and dexterity features are just as important as form, size, and facial characteristics. These elements provide essential insights into a robot's capabilities. A robot that moves smoothly and swiftly may signal efficiency and competence, promoting a positive interaction. On the flip side, a robot that struggles with mobility might discourage users from engaging due to perceived incompetence. How a robot moves can evoke feelings of reliability, while its ability to manipulate objects suggests skill and effectiveness. The intersection of these elements creates a complex web of interaction dynamics.
Psychological and Emotional Responses to Different Robot Designs
Psychological responses to robot designs can heavily influence trust and comfort levels. When a robot's appearance feels familiar or friendly, users tend to trust it more, leading to smoother interactions. This trust can be especially critical in settings like healthcare or service industries, where emotional bonds may enhance the overall experience. Conversely, designs that feel alien or overly mechanical can create unease. Users might second-guess a robot's capabilities if its form does not resonate positively.
Moreover, perceived intelligence and competency also emerge from robot designs. A polished, sophisticated appearance can lead individuals to see a robot as more competent, which in turn can enhance collaboration. If a robot looks well-designed and innovative, people usually expect it to function effectively, leading to increased reliance on its capabilities. However, if the design looks outdated or clunky, it may prompt doubt regarding its intelligence. This relationship between design and perceived function is crucial in determining how humans will utilize a robot in various applications.
Emotional attachment can also be significant in interactions with robots. People often form connections based on a robot's design and behavior. For instance, a robot that seems to respond emotionally may elicit empathy, fostering a relationship-like dynamic. This emotional engagement can lead to continued interactions, even outside of necessary contexts. It's fascinating how a robot designed with warmth can help individuals overcome feelings of loneliness, establishing bonds similar to those with pets or companions.
The Uncanny Valley Effect
The uncanny valley is a phenomenon where robots that closely resemble humans evoke unease instead of comfort. This effect occurs when a robot’s appearance is nearly, but not quite, human-like. It triggers a sense of eeriness; users may feel repulsed even as the robot maintains human features. Understanding this concept is essential for designers to create robots that are not only effective but also positively perceived. The uncanny valley highlights how important it is to strike the right balance between human-like features and mechanical attributes.
There are several case studies that illustrate the uncanny valley effect in robotics. For example, researchers tested how subjects reacted to different types of humanoid robots, revealing that slight alterations in facial details affected emotional responses drastically. A robot that is too lifelike may invite suspicion or discomfort, while one that is obviously robotic and functional receives a more positive response. This underscores the need for thoughtful design to avoid crossing into the uncanny valley.
Design strategies to mitigate negative reactions include creating more stylized robots that focus on functionality over realism. Designers can emphasize specific features, like a friendly face or vibrant colors, while avoiding overly realistic portrayals. Balance is key; incorporating familiar elements while maintaining a clear distinction between robot and human can lead to more favorable responses. By understanding the uncanny valley, creators can develop robots that people feel comfortable interacting with, ultimately leading to a better user experience.
Functional Versus Aesthetic Design Priorities
Finding a balance between practicality and aesthetic appeal is a challenge in robot design. On one hand, functionality is crucial; a robot must perform tasks effectively. On the other hand, an appealing design can significantly enhance user acceptance. Striking this balance allows for robots that not only work well but also encourage user interaction. Designers must consider how the aesthetics will influence the perception of the robot's capabilities. The goal should be to create an inviting yet efficient machine.
Industry-specific design considerations also shape how robots are created. Different fields, such as healthcare or education, have unique requirements; a robot working in a hospital might need a sterile, sleek appearance, while a robot designed for a classroom may lean more towards friendly, approachable features. These variations drive home the point that not all environments call for the same design approaches. Knowing the target audience plays a crucial role in these decisions.
User-centered design approaches are increasingly important in evaluating robot appearances. Understanding what users want and need allows for better alignment with public expectations. Designers can gather feedback during the development process, ensuring the end product resonates with consumers. By prioritizing usability and comfort alongside aesthetics, developers can create robots that support enhanced interaction and communication. Ultimately, this focus leads to better acceptance and success in the market.
Impact of Robot Appearance on Communication and Interaction Quality
The appearance of robots significantly influences communication dynamics. Robots designed with human-like attributes tend to enhance verbal interactions, as users often feel more comfortable engaging with them. Friendly robotic designs can elicit more open conversations, fostering deeper engagement. This quality of interaction is vital in environments where the robot's role is to provide assistance or facilitate exchanges. Clear features can encourage users to share information confidently, crucial for collaborative tasks.
Non-verbal communication cues also play a crucial role in how humans interact with robots. Facial expressions, gestures, and even posture convey messages beyond words. A robot that nods or tilts its head in response may come across as engaged and attentive. These cues can help bridge the gap between human and machine, prompting a more natural flow of interaction. If a robot reflects appropriate emotional responses, it can enhance communication quality by making users feel understood and valued.
Collaboration and teamwork with robots are heavily influenced by design. When a robot's appearance aligns with its functionality, users are more likely to see it as a reliable partner. Effective designs can promote a sense of shared purpose, enhancing the overall teamwork experience. A well-designed robot can become an integral part of a team, leading to improved efficiency and teamwork quality. In scenarios where the robot performs tasks with human partners, strong design choices can foster trust and reliability, essential for successful collaboration.
Long-Term Effects of Robot Appearance on Human Acceptance
The long-term effects of robot appearance are becoming increasingly relevant as robotics technology advances. Changes in social norms and behaviors often reflect society's adapting attitudes toward robots. As robots become more integrated into daily life, people's acceptance can shift dramatically. Over the years, as users grow accustomed to different robot designs, their previous apprehensions may diminish. It is fascinating to observe how cultural perceptions can evolve and how familiarity can breed acceptance.
The evolution of robot design over time provides insights into these changing attitudes. Early robots often aimed for purely functional designs, but the trend now includes more human-like features. As users engage more with robots, designers increasingly focus on aesthetics to align with public expectations. This evolution reflects a deeper understanding of how appearance affects interaction and acceptance. Each technological advancement encourages a reevaluation of design priorities, responding to user needs and preferences.
Looking ahead, we can predict future dynamics of human-robot interaction. As technology continues to advance, we will likely see robots with greater emotional intelligence and adaptability. This will further blur the lines between human and machine, pushing the boundaries of interaction quality. As societal norms evolve, we may also witness a shift in how we perceive autonomous machines. Embracing robots that feel more like companions rather than mere tools could transform our interaction landscape, fostering greater collaboration and acceptance in the years to come.